




1. What is WOL and what is its function?
WOL stands for Wake-on-LAN, meaning “LAN Wake-up.” It is a network technology that enables remote wake-up of computers or devices from sleep, standby, or shutdown states over a network. (Note: This requires devices supporting low-power network standby after shutdown.) This technology significantly enhances IT management flexibility, allowing administrators to restart or power on devices anytime without physical access.
2. Application Scenarios for WOL
Convenient Management: Enables enterprise IT teams to remotely power on devices for maintenance, software upgrades, and patch deployment, reducing on-site operational costs.
Remote Work: Employees can remotely wake office computers from home and access them via remote desktop, boosting productivity.
Smart Home: Enables remote activation of NAS (network-attached storage), home media servers, and other devices, minimizing unnecessary energy consumption.
Industrial Automation: Facilitates remote startup of industrial control systems, reducing manual intervention and enhancing automation levels.
3.Wake-on-LAN Architecture
Primarily consists of the following components:
① Target Computer (Wake-Up Device)
Requires a motherboard and BIOS/UEFI supporting WOL, with relevant settings enabled—such as the “Wake on LAN” option in BIOS and corresponding configurations in the network adapter driver.
② WOL-enabled Network Interface Card (NIC)
Remains in low-power state while monitoring for specific Magic Packets when the computer is powered off or in hibernation.
③ Network (LAN or WAN)
Typically used over wired Ethernet networks, though remote WOL can be achieved via VPN or public port forwarding.
④ WOL Sender (Control End)
Runs WOL client software (e.g., wol command, third-party WOL tools) or is embedded within enterprise IT device management systems to send Magic Packets and wake target computers.
4. Illustrative Examples
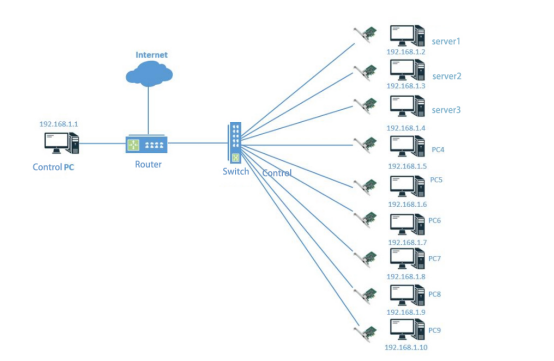
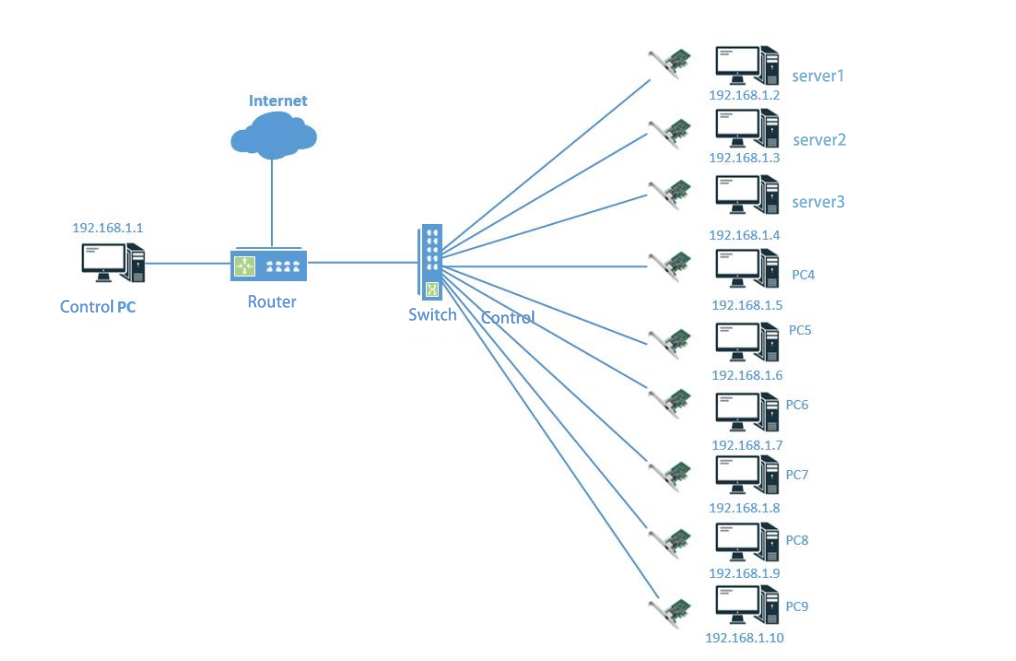
In enterprise office network environments (as shown in the diagram, where multiple servers, PCs, and other devices are connected via switches and routers), Wake-on-LAN (WOL) technology can be applied. For instance, during non-working hours, servers and some PCs remain powered off or in standby mode to conserve energy. When the work period begins, the control PC (IP: 192.168.1.1) can utilize the WOL function to send wake-up packets to servers such as Server 1 (192.168.1.2) and Server 2 (192.168.1.3), as well as PCs like PC4 (192.168.1.5) and PC5 (192.168.1.6). Upon receiving these packets, the devices rapidly boot from shutdown or standby mode. This enables employees to immediately begin working without manually powering each device individually, enhancing office efficiency while facilitating centralized management and scheduling of the entire network infrastructure.
